 Functions
Functions
 random number (0 <= x < 1)
random number (0 <= x < 1)
The random number returns the value of 0 till the number entered. Without specifying the range, the random number returns 0 till 1. The interval of possible random number values includes zero, but it does not include the terminal value. For example, for the implicit interval 0 till 1 the resulting random number can reach the value of 0, but it can never reach the value of 1, the number being always close below the value of 1 as the maximum.
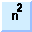 square power
square power
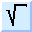 square root
square root
 absolute value
absolute value
 integer part
integer part
 fractional part
fractional part
 increment
(adds 1)
increment
(adds 1)
 decrement
(subtracts 1)
decrement
(subtracts 1)
The function of splitting the number in the integer and the fractional part does not depend on the sign, int(-x) = -int(x).
 sine
sine
 cosine
cosine
 tangent
tangent
 cotangent
cotangent
 arcsine
arcsine
 arccosine
arccosine
 arctangent
arctangent
 arccotangent
arccotangent
 convert degrees to radians
convert degrees to radians
 convert radians to degrees
convert radians to degrees
The goniometric functions calculations are carried out in radian. If a calculation in degree is required, the function converting degrees and radians may be used.
 decadic logarithm
decadic logarithm
 natural logarithm
natural logarithm
 natural exponential function
natural exponential function
 factorial
factorial
The factorial calculation is carried out for an argument that is rounded up to the nearest integer value. The valid factorial argument ranges between -170 and +170. For negative argument values the calculation result for an odd number is negative, for an even number positive (odd or even number of multiplication operations).
 distance of point
distance of point
 X coordinate of point
X coordinate of point
 Y coordinate of point
Y coordinate of point
The distance of point function serves to calculate a point’s distance from the coordinate system origin or mutual distances of two points. As parameters the point’s coordinates or the two points‘ coordinate differences are specified.
 angle of point
angle of point
 X coordinate of point
X coordinate of point
 Y coordinate of point
Y coordinate of point
The angle of point function serves to calculate the point angle from the X-axis of the coordinate system or to calculate the angle of the direction defined by two points. As parameters the point’s coordinates or the two points‘ coordinate differences are specified.